What Does the Check Engine Light Mean?
Imagine you’re driving, and suddenly, a small amber light shaped like an engine illuminates on your dashboard. The check engine light can be unsettling, leaving you wondering if it’s a minor glitch or a major issue. This warning system is your car’s way of signaling that something is wrong within its engine or emissions system.
Ignoring the light could lead to worsening problems, such as decreased fuel efficiency or even costly engine damage. The causes range from a simple loose gas cap to more complex issues like a failing catalytic converter. By identifying the root cause promptly, you can save time, money, and potential headaches.
This article will explore the top causes of a check engine light, steps to take when it turns on, and preventive measures to keep your vehicle in top condition. Whether you’re a seasoned car owner or a beginner, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to address the problem effectively.
Top 10 Causes of a Check Engine Light
When your check engine light comes on, it’s essential to understand what could be triggering it. Below, we dive into the top causes of a check engine light, explaining the symptoms, consequences, and potential fixes for each.
1. Loose Gas Cap
A simple yet common cause of the check engine light is a loose or damaged gas cap. This component seals the fuel system and maintains pressure, preventing fuel vapor leaks.
- Symptoms: Slight decrease in fuel efficiency, gasoline smell.
- Why It Triggers the Light: The onboard diagnostic system detects an evaporative emission leak.
- Fix: Ensure the gas cap is tightened. If damaged, replace it with a new one.
Pro Tip: Tighten the cap until it clicks to ensure a proper seal.
2. Faulty Oxygen Sensor

The oxygen sensor monitors the amount of unburned oxygen in your vehicle’s exhaust. A malfunctioning sensor can lead to inaccurate air-fuel mixture readings.
- Symptoms: Poor fuel economy, rough idling, or engine misfiring.
- Why It Triggers the Light: The engine control unit (ECU) cannot adjust the fuel mixture properly.
- Fix: Replace the faulty sensor promptly.
Fun Fact: Most vehicles have multiple oxygen sensors—one for each exhaust manifold.
3. Catalytic Converter Malfunction
The catalytic converter reduces harmful emissions by converting them into less toxic substances. A failure here can significantly impact performance and emissions.
- Symptoms: Rotten egg smell, reduced acceleration, or failed emissions tests.
- Why It Triggers the Light: Excessive emissions or low efficiency detected by oxygen sensors.
- Fix: If cleaning doesn’t work, replacement may be necessary—though costly.
Tip for Prevention: Regular maintenance and timely repairs of the exhaust system help extend the lifespan of the catalytic converter.
4. Mass Airflow Sensor Issues
The mass airflow sensor (MAF) measures the amount of air entering the engine to optimize the air-fuel ratio.
- Symptoms: Stalling, hesitation during acceleration, or trouble starting.
- Why It Triggers the Light: Incorrect air measurements lead to improper fuel delivery.
- Fix: Clean the MAF sensor with a specialized cleaner or replace it if defective.
Insight: Dirty air filters can often lead to MAF sensor problems—replace them regularly.
5. Spark Plug and Ignition Coil Problems

The spark plugs ignite the air-fuel mixture, and ignition coils supply the required voltage. Faults here disrupt engine combustion.
- Symptoms: Misfires, poor acceleration, or rough idling.
- Why It Triggers the Light: Misfires are detected by the ECU, affecting performance and emissions.
- Fix: Replace spark plugs and coils according to your vehicle’s maintenance schedule.
Maintenance Tip: Use high-quality spark plugs for better durability and efficiency.
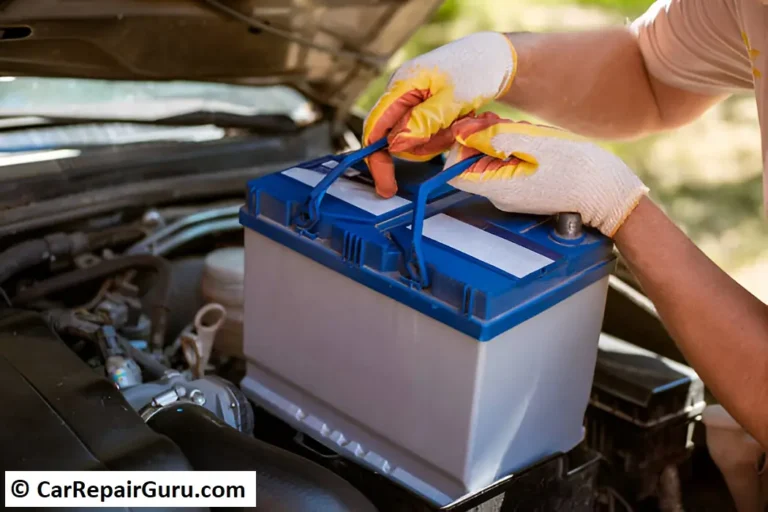
6. Battery or Alternator Failure
A weak battery or failing alternator can disrupt the electrical system, affecting engine performance.
- Symptoms: Dim headlights, slow engine cranking, or electrical malfunctions.
- Why It Triggers the Light: Insufficient voltage to essential systems.
- Fix: Test and replace the battery or alternator as needed.
Note: Batteries should be checked regularly, especially before extreme weather conditions.
7. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve Malfunction
The EGR valve recirculates a portion of exhaust gases back into the engine to reduce nitrogen oxide emissions.
- Symptoms: Engine knocking, decreased performance, or stalling.
- Why It Triggers the Light: Blockages or valve failure affect emissions and combustion.
- Fix: Clean or replace the EGR valve as required.
Efficiency Tip: Use quality fuel to minimize carbon deposits on the EGR valve.
8. Evaporative Emission Control (EVAP) System Faults

The EVAP system prevents fuel vapors from escaping into the atmosphere. Issues here are common culprits for a check engine light.
- Symptoms: Gasoline smell, trouble starting, or reduced fuel efficiency.
- Why It Triggers the Light: Vapor leaks or sensor malfunctions.
- Fix: Inspect hoses and valves for damage or leaks and replace them.
Diagnostic Tip: Use a smoke test to pinpoint leaks in the EVAP system.
9. Transmission Problems
The transmission ensures your engine delivers power to the wheels efficiently. Faults here can affect vehicle performance and trigger a warning.
- Symptoms: Difficulty shifting gears, slipping, or overheating.
- Why It Triggers the Light: Sensors detect abnormal gear ratios or performance issues.
- Fix: Get the transmission checked and serviced by a professional.
Preventive Tip: Change transmission fluid at recommended intervals to avoid costly repairs.
10. Intake Vacuum Leaks
Vacuum leaks occur when air enters the engine through unintended gaps, disrupting the air-fuel ratio.
- Symptoms: Hissing noise, high idle speed, or engine stalling.
- Why It Triggers the Light: The ECU senses an improper air mixture.
- Fix: Locate and seal leaks in hoses or intake manifolds.
Note: Regular inspections of hoses and gaskets can prevent leaks.
Each of these causes contributes uniquely to the check engine light warning. By addressing the issue early, you can maintain your vehicle’s health, improve fuel economy, and avoid more significant repair costs down the road.
What to Do When Your Check Engine Light Comes On

The check engine light is your car’s way of alerting you to a potential problem. While it can be unnerving, not all causes require immediate or costly repairs. Here’s a step-by-step guide on what to do when this warning light appears.
1. Stay Calm and Observe
- Primary Keyword Use: A check engine light doesn’t always indicate a severe issue. Begin by noting whether the light is solid or blinking:
- Solid Light: Usually points to non-urgent issues like a loose gas cap or an emissions sensor problem.
- Blinking Light: Indicates a serious problem, such as an engine misfire, that requires immediate attention.
Tip: Pull over safely if you notice any unusual sounds, smells, or reduced performance.
2. Check the Gas Cap
One of the simplest causes of a check engine light is a loose or damaged gas cap. A poorly sealed cap can lead to fuel vapor escaping, triggering an emissions system warning.
- Tighten the cap until it clicks.
- Inspect it for cracks or damage.
Quick Fix: If tightening the cap doesn’t resolve the issue, consider replacing it with a new one.
3. Use an OBD-II Scanner to Read Trouble Codes
Modern vehicles are equipped with an On-Board Diagnostics (OBD-II) system that stores trouble codes when a fault is detected. An OBD-II scanner can help you identify the issue.
- Steps:
- Plug the scanner into the OBD-II port (usually located under the dashboard).
- Turn on the ignition but don’t start the car.
- Read the codes displayed on the scanner.
- Common Codes:
- P0457: Loose gas cap.
- P0135: Oxygen sensor issue.
- P0420: Catalytic converter problem.
DIY Option: Affordable OBD-II scanners are available online and can save you a trip to the mechanic.
4. Decide Between DIY Fixes and Professional Help
Some issues, like replacing a gas cap or cleaning an oxygen sensor, can be handled at home. However, more complex problems, such as transmission failures or catalytic converter malfunctions, may require expert attention.
- DIY Fixes:
- Replace spark plugs or ignition coils.
- Clean or replace air filters.
- Tighten or replace hoses causing vacuum leaks.
- When to Call a Mechanic:
- Persistent or recurring codes after DIY fixes.
- Signs of severe engine damage (e.g., smoke, knocking sounds).
- Electrical issues or transmission failures.
Pro Tip: For serious issues, opt for a professional diagnostic at a trusted repair shop.
5. Reset the Check Engine Light (If Appropriate)
Once the issue is resolved, you can reset the light using an OBD-II scanner. Keep in mind that if the underlying problem persists, the light will reappear.
- Steps to Reset:
- Fix the detected issue.
- Use the OBD-II scanner’s “clear codes” function.
- Drive the car for a few miles to ensure the issue is resolved.
Important Note: Avoid resetting the light to mask problems—it can lead to more significant repairs later.
6. Prevent Future Check Engine Light Issues
Preventive maintenance is key to avoiding unexpected warnings:
- Stick to your vehicle’s maintenance schedule.
- Replace spark plugs, air filters, and fluids regularly.
- Invest in high-quality fuel and parts to minimize wear.
Preventive Tip: Periodic diagnostic scans can catch minor issues before they escalate.
Addressing check engine light causes promptly not only ensures your vehicle’s reliability but also prevents costly repairs down the road. By following these steps, you’ll be equipped to handle the next dashboard warning like a pro.
The Risks of Ignoring Check Engine Light Causes

The check engine light is more than an annoying dashboard feature—it’s a critical warning system for your vehicle. Ignoring it can lead to severe consequences, affecting your car’s performance, safety, and environmental impact. Here’s why addressing the issue promptly is crucial:
1. Long-Term Vehicle Damage
When the check engine light signals a problem, it often indicates an issue that can escalate if left unaddressed. For instance:
- Catalytic Converter Failure: A faulty oxygen sensor or unresolved misfire can damage the catalytic converter, a costly component to replace.
- Engine Damage: Persistent misfires or overheating may cause permanent damage to the engine’s internal components, such as the pistons or cylinders.
Fact: Repairing a minor sensor issue costs significantly less than rebuilding or replacing an engine damaged by neglect.
2. Safety Concerns
Certain check engine light causes can compromise the safety of your vehicle, including:
- Transmission Failures: Ignoring transmission-related warnings can result in sudden gear slippage or power loss while driving, increasing the risk of accidents.
- Brake System Faults: Some codes may signal an indirect issue affecting braking performance, especially in modern cars where systems are interconnected.
Tip: If the light is blinking, it indicates an urgent problem that could put your safety at risk. Pull over and seek professional help immediately.
3. Increased Emissions and Environmental Harm
A malfunctioning exhaust or emissions system can lead to:
- Higher Pollutant Output: Issues like a failed catalytic converter or leaky EVAP system increase harmful emissions, contributing to environmental damage.
- Failed Emissions Tests: Vehicles with an active check engine light often fail inspections, resulting in fines or restrictions on driving until repairs are completed.
Impact: Regular maintenance reduces emissions, supporting cleaner air and compliance with environmental laws.
Why You Should Act Now
Ignoring the check engine light can turn minor issues into costly repairs and pose serious safety hazards. Addressing the problem early protects your car, your wallet, and the environment.
By staying proactive, you ensure your vehicle remains reliable, efficient, and safe for years to come.
Preventing Check Engine Light Issues

Preventing a check engine light from coming on requires consistent care and attention to your vehicle. By following these vehicle maintenance tips, you can minimize the likelihood of unexpected problems and keep your car running smoothly.
1. Stick to a Regular Maintenance Schedule
Routine tune-ups and inspections are essential for preventing issues:
- Replace air and fuel filters as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Ensure oil changes are performed at the specified intervals to keep the engine lubricated and clean.
Tip: Follow the maintenance schedule in your owner’s manual to avoid missing critical services.
2. Keep an Eye on Warning Signs
Many issues that trigger the check engine light can be caught early through careful observation:
- Listen for unusual sounds like knocking or hissing.
- Check for physical signs such as leaks or wear on belts and hoses.
Pro Tip: Address minor issues promptly to prevent them from escalating into major repairs.
3. Replace Worn Parts on Time
Faulty components often lead to check engine light causes like sensor failures or misfires. Focus on:
- Replacing spark plugs and ignition coils every 30,000–50,000 miles.
- Inspecting and replacing the oxygen sensor and mass airflow sensor as needed.
4. Use High-Quality Fuel and Parts
Low-quality fuel can cause deposits in the engine, leading to clogged components. Similarly, cheap replacement parts may fail prematurely, causing additional problems.
Tip: Invest in quality to ensure longevity and performance.
5. Protect the Emissions System
Avoid overfilling the gas tank and ensure the gas cap is tightened properly. Regularly check for leaks in the exhaust system to maintain compliance with emissions standards.
By adopting these preventive measures, you’ll not only avoid the check engine light but also enjoy better performance, improved fuel efficiency, and a longer vehicle lifespan.
Conclusion
The check engine light is an essential indicator of your vehicle’s health, alerting you to both minor and critical issues. Ignoring it can lead to costly repairs, safety risks, and environmental harm. By addressing the underlying causes promptly, you can ensure your vehicle remains reliable, efficient, and safe to drive.
Routine vehicle maintenance, timely part replacements, and understanding how to respond when the light comes on are key to preventing and managing potential problems. Tools like OBD-II scanners empower you to diagnose issues early, saving you time and money.
Incorporating these practices into your car care routine not only prevents the light from coming on but also enhances your driving experience, prolongs your car’s lifespan, and protects the environment. When it comes to the check engine light, proactive care is always the best approach.
check engine light FAQ Section
Why is my check engine light blinking?
A blinking check engine light signals a severe issue, often related to engine misfires or unburned fuel damaging the catalytic converter. Stop driving immediately and seek professional help to avoid further damage or safety risks.
Can I drive with the check engine light on?
If the light is solid, you may continue driving short distances but should address the issue promptly. A blinking light, however, indicates a serious problem, and driving in this condition can cause significant engine damage or safety hazards.
How do I reset my check engine light?
To reset the check engine light, use an OBD-II scanner to clear the codes after resolving the issue. Alternatively, disconnect the battery for a few minutes to reset the system. Keep in mind that if the problem persists, the light will return.
What does a solid check engine light mean?
A solid check engine light typically indicates non-urgent issues, such as a loose gas cap, a faulty sensor, or emissions-related faults. While not critical, these problems should be inspected and resolved to maintain vehicle performance.
What causes the check engine light to come on after rain?
Moisture can affect electrical components like sensors or the ignition system, triggering the light. Check for wet or corroded connections, especially around the engine and battery, and dry them thoroughly to resolve the issue.