Modern vehicles are more than just machines with engines and wheels—they are intelligent systems packed with advanced electronics that enhance performance, safety, and efficiency. At the heart of this evolution is the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), a small yet powerful computer responsible for managing various functions within a vehicle.
Over the past few decades, automotive electronics have drastically changed, shifting from mechanical components to sophisticated vehicle control systems. Early cars relied on manual adjustments, but today’s vehicles incorporate multiple ECUs, each dedicated to a specific function, such as engine control, transmission management, and braking systems. This transition has led to improved fuel efficiency, better driving experiences, and safer roads.
Whether it’s optimizing engine performance, controlling infotainment systems, or managing safety features, ECUs play a crucial role in modern automobiles. But what exactly is an ECU, and how does it work? Let’s dive deeper into the brains behind your vehicle’s smart functionality.
What is an Electronic Control Unit (ECU)?
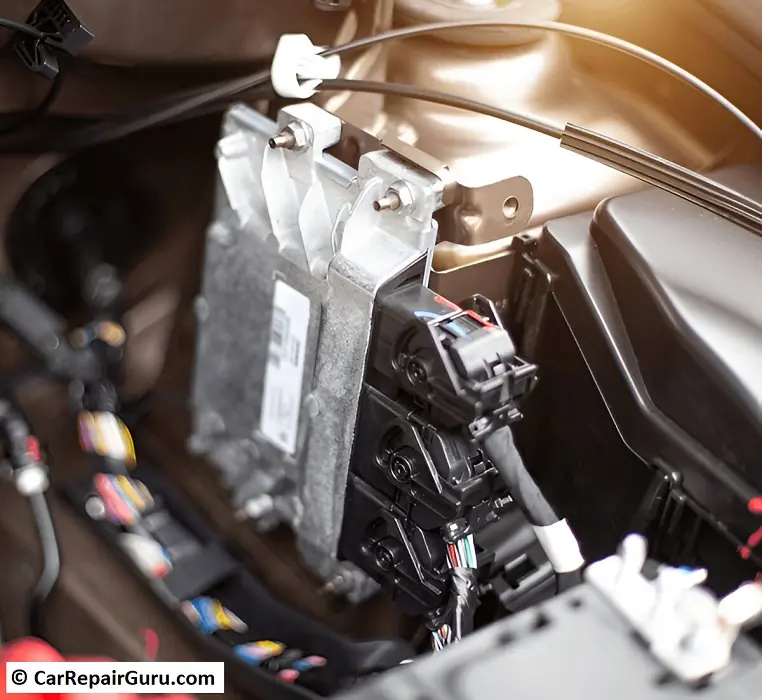
An Electronic Control Unit (ECU) is a specialized computer that manages and controls various electronic systems in a vehicle. Acting as the brain of modern automobiles, the ECU processes data from multiple sensors, makes real-time decisions, and sends commands to different components to optimize performance, efficiency, and safety.
From Mechanical to Electronic: The Evolution of Vehicle Control
In the past, cars relied on mechanical systems for essential functions like fuel delivery, braking, and ignition timing. These components required manual adjustments and were less precise. However, with advancements in automotive electronics, ECUs have replaced mechanical controls, offering greater accuracy, automation, and adaptability.
For example, older vehicles used carburetors to mix air and fuel, often requiring manual tuning. Today, Engine Control Units (ECMs) regulate fuel injection electronically, adjusting the mixture based on real-time data from oxygen sensors, ensuring optimal performance and fuel economy.
The Impact of ECUs on Modern Vehicles
Thanks to ECUs, vehicles have become smarter, safer, and more efficient. These advanced systems help manage:
✔ Engine performance for better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
✔ Transmission shifts for smoother driving and power optimization.
✔ Braking systems, including ABS and electronic stability control, for improved safety.
✔ Infotainment and navigation, offering seamless digital experiences.
In essence, ECUs have revolutionized how vehicles operate, making driving more automated, responsive, and intelligent than ever before.
How Does an Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Work?
An Electronic Control Unit (ECU) functions as the brain of a vehicle, continuously processing data from sensors and making real-time decisions to optimize performance, safety, and efficiency. But how exactly does it work? Let’s break it down.
Key Components of an ECU
An ECU consists of three primary components:
Microcontroller (Processor): The core computing unit that processes incoming data, runs algorithms, and makes decisions. Think of it as the ECU’s brain.
Input/Output Interfaces: These allow the ECU to receive data from sensors and send commands to actuators, controlling various vehicle functions.
Software & Firmware: The ECU runs on specialized programs that determine how it interprets sensor data and responds. These programs can be updated or reprogrammed to improve functionality.
How an ECU Processes Data
An ECU follows a three-step cycle to control vehicle operations:
1. Data Collection from Sensors
Modern vehicles have hundreds of sensors that monitor critical aspects like engine temperature, air intake, throttle position, wheel speed, and braking pressure. These sensors constantly send real-time data to the ECU.
2. Decision-Making & Processing
The ECU processes the incoming data using pre-programmed algorithms. For instance:
- If the oxygen sensor detects too much fuel in the air-fuel mixture, the ECU adjusts fuel injection to improve efficiency.
- If the wheel speed sensor detects sudden braking, the ECU activates the ABS system to prevent skidding.
3. Sending Commands to Actuators
After processing the data, the ECU sends signals to actuators (such as fuel injectors, throttle valves, or braking systems) to execute the necessary adjustments.
How ECUs Optimize Vehicle Performance
Thanks to this continuous feedback loop, ECUs:
✅ Enhance fuel efficiency by adjusting air-fuel ratios dynamically.
✅ Improve safety through traction control, electronic stability control, and adaptive braking systems.
✅ Optimize transmission shifts for smoother driving.
✅ Reduce emissions by regulating combustion more precisely.
In short, ECUs turn raw sensor data into intelligent actions, making vehicles smarter, safer, and more efficient than ever.
Types of Electronic Control Units in Vehicles

Modern vehicles rely on multiple Electronic Control Units (ECUs), each dedicated to a specific function. While early cars had only one or two ECUs, today’s vehicles can have 50 to 150 ECUs, all working together to enhance performance, safety, and comfort. Below are the most critical ECUs found in modern vehicles.
1. Engine Control Module (ECM) – The Heart of Engine Performance
The Engine Control Module (ECM), also known as the Engine Control Unit (ECU), is one of the most vital components in a car. It:
✔ Monitors sensors like the oxygen sensor, mass airflow sensor, and throttle position sensor.
✔ Adjusts the air-fuel ratio for better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
✔ Controls ignition timing and idle speed to enhance performance.
✔ Diagnoses and logs engine faults through the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) system.
By continuously optimizing these functions, the ECM ensures smooth and efficient engine operation.
2. Transmission Control Module (TCM) – Smoother Shifting & Performance
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) manages automatic gear shifting and optimizes transmission performance. It:
✔ Collects data from speed sensors, throttle sensors, and engine load sensors.
✔ Ensures seamless gear changes for fuel efficiency and a smooth ride.
✔ Protects the transmission from damage by adjusting shifts based on driving conditions.
For automatic and dual-clutch transmissions, the TCM is essential for improving fuel economy and acceleration.
3. Brake Control Module (BCM) – Enhancing Safety & Stability
The Brake Control Module (BCM) is responsible for managing braking systems like:
✔ Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) – Prevents wheels from locking up during sudden braking.
✔ Electronic Stability Control (ESC) – Helps maintain vehicle stability during sharp turns or slippery conditions.
✔ Traction Control System (TCS) – Prevents wheel spin by adjusting braking force and engine power.
These systems improve safety and braking efficiency, reducing the risk of accidents.
4. Body Control Module (BCM) – The Comfort & Convenience Manager
The Body Control Module (BCM) controls various electronic accessories and body-related functions, including:
✔ Power windows, mirrors, and locks.
✔ Interior and exterior lighting.
✔ Climate control systems.
✔ Security features like keyless entry and alarm systems.
This ECU plays a significant role in ensuring driver and passenger comfort.
5. Infotainment Control Module – The Digital Experience Hub
The Infotainment Control Module manages entertainment, navigation, and connectivity systems in modern cars. It:
✔ Controls touchscreens, audio systems, and GPS navigation.
✔ Supports Bluetooth, Apple CarPlay, and Android Auto for hands-free communication.
✔ Integrates with voice assistants and smart vehicle functions.
This module transforms driving into a more connected and enjoyable experience.
The Growing Role of ECUs in Modern Vehicles
With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving, and smart car technology, the number of ECUs in cars is increasing rapidly. Advanced vehicles now feature ECUs for:
✔ Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) like lane-keeping assist and adaptive cruise control.
✔ Battery Management Systems (BMS) in electric vehicles to regulate charging and energy distribution.
✔ Autonomous driving features, requiring ECUs to process vast amounts of real-time data.
As vehicles become more intelligent and connected, ECUs will continue to play an even bigger role in shaping the future of transportation.
Importance of Electronic Control Units in Modern Vehicles
Electronic Control Units (ECUs) are the backbone of modern vehicle technology, ensuring safety, efficiency, and automation. Without ECUs, today’s cars wouldn’t have the advanced features that improve driving experiences and reduce environmental impact.
1. Enhancing Vehicle Safety Features
ECUs are critical in modern safety systems, providing real-time monitoring and response to road conditions. Key safety features managed by ECUs include:
✔ Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) – Prevents wheel lock-up, allowing controlled braking.
✔ Electronic Stability Control (ESC) – Helps maintain traction and stability in slippery conditions.
✔ Traction Control System (TCS) – Prevents excessive wheel spin during acceleration.
✔ Airbag Deployment Systems – Instantly detects crashes and deploys airbags for protection.
These systems reduce accidents and improve road safety, protecting both drivers and passengers.
2. Improving Fuel Efficiency & Emission Control
ECUs optimize fuel injection, combustion, and exhaust systems, leading to:
✔ Better fuel economy by adjusting air-fuel mixtures dynamically.
✔ Lower emissions through precise engine control, reducing pollutants.
✔ Hybrid & Electric Vehicle (EV) Efficiency – Managing battery usage and energy distribution in electric and hybrid vehicles.
With stricter emission regulations, ECUs play a crucial role in making vehicles eco-friendlier.
3. Powering Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
ADAS features rely on multiple ECUs working together to assist drivers with:
✔ Adaptive Cruise Control – Automatically adjusts speed based on traffic.
✔ Lane-Keeping Assist – Helps drivers stay centered in their lane.
✔ Blind-Spot Monitoring – Alerts drivers to unseen vehicles nearby.
These systems enhance driving safety and comfort, reducing human error.
4. Contributing to Autonomous Driving
Self-driving technology depends on ECUs to process data from cameras, LiDAR, and sensors. ECUs analyze road conditions, traffic, and obstacles in real time, making autonomous vehicles possible.
As AI-driven ECUs evolve, they will pave the way for fully self-driving cars, revolutionizing transportation.
In short, ECUs have transformed the automotive industry, making cars smarter, safer, and more efficient than ever before.
Common Issues and Maintenance of Electronic Control Units (ECUs)

While Electronic Control Units (ECUs) are designed to be highly reliable, they can develop issues over time due to electrical faults, software glitches, or physical damage. Identifying problems early and maintaining the ECU properly can prevent costly repairs and vehicle performance issues.
1. Signs of a Failing ECU
If your ECU is malfunctioning, you may notice the following warning signs:
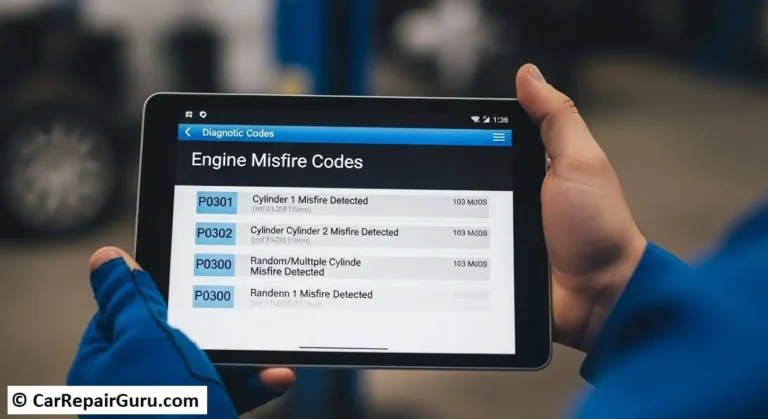
✔ Check Engine Light (CEL) Stays On – A persistent CEL could indicate an ECU error or failure.
✔ Poor Engine Performance – Erratic idling, misfires, or power loss may signal an ECU issue.
✔ Starting Problems or Stalling – A faulty ECU can cause the engine to struggle to start or shut off unexpectedly.
✔ Unusual Fuel Consumption – An ECU failure may disrupt fuel injection timing, reducing efficiency.
✔ Transmission Issues – In vehicles with electronic transmissions, ECU faults can lead to rough shifting or gear slippage.
Ignoring these signs can lead to further vehicle damage, so timely diagnostics are essential.
2. Diagnosing ECU Problems
To diagnose ECU issues, mechanics use specialized tools and techniques, including:
✔ OBD-II Scanner – Retrieves error codes from the ECU to pinpoint issues.
✔ Multimeter Testing – Measures voltage and resistance in ECU wiring.
✔ Software Reprogramming – Some ECU errors can be fixed with firmware updates.
A professional mechanic can reflash or replace a faulty ECU if needed.
3. ECU Maintenance Tips
To extend the lifespan of your ECU:
✔ Avoid Voltage Surges – Use a stable battery and avoid jump-starting incorrectly.
✔ Keep Wiring & Sensors Clean – Dirty or corroded connectors can lead to faulty signals.
✔ Protect Against Moisture & Heat – Excessive heat or water exposure can damage the ECU.
✔ Perform Regular Vehicle Inspections – Catch potential electrical problems before they worsen.
By following these tips, you can keep your ECU functioning optimally, ensuring better vehicle performance and reliability.
Future Trends in Electronic Control Unit (ECU) Technology
As automotive technology advances, Electronic Control Units (ECUs) are evolving to meet the growing demands of connectivity, automation, and electrification. Here’s what the future holds for ECU technology:
1. Centralized Vehicle Control Systems
Traditionally, vehicles had dozens of independent ECUs, each controlling specific functions. However, automakers are now shifting towards centralized computing architectures, which:
✔ Replace multiple ECUs with a few high-performance processors.
✔ Reduce wiring complexity, lowering vehicle weight and improving efficiency.
✔ Enable seamless communication between vehicle systems for smarter decision-making.
This trend paves the way for software-defined vehicles, where features can be updated via over-the-air (OTA) updates.
2. Advancements in ECU Software & Hardware
Modern ECUs are becoming more powerful, thanks to:
✔ AI-driven algorithms that optimize real-time performance.
✔ Faster processors that handle complex computations for ADAS and autonomous driving.
✔ Enhanced cybersecurity to protect against vehicle hacking threats.
Future ECUs will rely heavily on cloud computing and edge processing, enabling better data analysis and predictive maintenance.
3. ECUs in Electric & Autonomous Vehicles
With the rise of electric (EVs) and autonomous vehicles (AVs), ECUs are being designed to:
✔ Manage battery performance and energy distribution efficiently.
✔ Process vast amounts of data from LiDAR, cameras, and sensors for autonomous navigation.
✔ Improve vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication for smarter traffic management.
As automotive technology advances, ECUs will become the central nervous system of next-generation vehicles, shaping the future of mobility.
Conclusion – The Driving Force Behind Modern Vehicles
Electronic Control Units (ECUs) are the brain of modern vehicles, managing everything from engine performance to safety systems and infotainment. Their role in fuel efficiency, emissions control, and driver assistance technologies makes them essential for today’s cars.
Understanding and maintaining ECUs is crucial for ensuring optimal vehicle performance and longevity. As automotive technology evolves, ECUs will become even more advanced, supporting autonomous driving, electric vehicles (EVs), and AI-powered enhancements.
With ongoing innovations, ECUs will continue shaping the future of mobility, making vehicles smarter, safer, and more efficient than ever before.
FAQs
1. What does an Electronic Control Unit (ECU) do in a car?
An ECU is a small computer that manages specific systems or functions in a vehicle, such as engine performance, braking, or infotainment. It gathers data from sensors and makes real-time decisions to optimize performance and safety.
2. Can a car run with a faulty ECU?
In some cases, yes—but it can lead to poor performance, increased fuel consumption, or even engine stalling. A severely damaged ECU may prevent the vehicle from starting at all.
3. How do I know if my ECU is malfunctioning?
Common signs include the check engine light staying on, poor acceleration, rough idling, difficulty starting the car, and unusual fuel usage. A diagnostic scan tool can confirm ECU-related issues.
4. Can an ECU be repaired or does it need replacement?
It depends on the damage. Some ECUs can be repaired or reprogrammed with updated software. In more severe cases, a full replacement may be necessary.
5. How long does an ECU last?
Typically, an ECU can last the lifetime of the vehicle—around 10 to 20 years—if maintained properly. However, electrical issues, heat, and moisture exposure can shorten its lifespan.