When it comes to your vehicle’s steering, the steering gearbox is the unsung hero that ensures smooth, responsive control. This essential component translates the rotation of your steering wheel into the precise movement of your wheels, making every turn accurate and effortless.
Without it, driving would be a chaotic experience. Whether you’re navigating tight city streets or cruising on the highway, a well-maintained steering gearbox guarantees a safe and comfortable ride.
This guide delves into the functions of steering gearboxes, explores their varied types, and provides practical advice on maintenance and troubleshooting common issues. You’ll also discover the latest advancements in steering technology, helping you make informed decisions about repairs or upgrades.
Understanding how your steering system works empowers you to keep your vehicle in top shape and ensures you can spot potential issues before they escalate.
Functions of Steering Gearboxes
At the heart of your vehicle’s steering system lies the steering gearbox, a critical component responsible for converting the rotational motion of the steering wheel into the linear motion required to turn the wheels.
When you turn the steering wheel, it engages the steering shaft, which transmits rotational energy to the steering gearbox. Inside the gearbox, a system of gears and mechanisms amplifies this energy while maintaining precision. This amplified motion is then directed to the steering linkage, ultimately guiding the wheels in the desired direction.
Depending on the type of steering gearbox—such as rack and pinion, recirculating ball, or worm and sector—the mechanics may vary slightly, but the principle remains the same. For example, a rack and pinion system uses a gear to slide a toothed bar (the rack) back and forth, creating the linear motion needed to steer.
By providing control and stability, the steering gearbox ensures a seamless driving experience. A well-functioning gearbox translates minor movements of the steering wheel into precise wheel adjustments, giving drivers confidence in every maneuver.
Understanding this function helps drivers appreciate the engineering behind safe, responsive steering.
Types of Steering Gearboxes
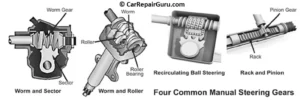
Steering gearboxes come in various types, each designed to meet specific vehicle needs. Let’s explore three common types:
Worm and Sector Gearbox
The worm and sector gearbox uses a worm gear attached to the steering shaft and a sector gear that engages with the worm. When the steering wheel is turned, the worm gear rotates, moving the sector gear to steer the wheels. This type of gearbox was popular in older vehicles due to its simplicity and durability. While not as common today, it is still found in heavy-duty vehicles and machinery where strength is prioritized over precision.
Recirculating Ball Gearbox
In this design, a series of ball bearings recirculate within the grooves of the worm gear. These ball bearings reduce friction, ensuring smoother operation. The recirculating ball gearbox is a preferred choice for larger vehicles such as trucks and SUVs, as it can handle higher loads and provides a robust, reliable steering mechanism.
Rack and Pinion Gearbox
The rack and pinion system is the most common in modern cars. It uses a pinion gear that meshes with a linear rack. When the steering wheel turns, the pinion gear moves the rack, translating rotational motion into linear motion. This design is lightweight, compact, and offers excellent precision, making it ideal for passenger cars and sports vehicles.
Understanding the differences between these gearboxes can help drivers make informed decisions about maintenance and upgrades.
Common Issues and Symptoms of Steering Gearboxes
A malfunctioning steering gearbox can significantly affect your driving experience and safety. Recognizing common issues early can prevent costly repairs and ensure smoother operation. Here are some typical problems to watch for:
Excessive Play in the Steering Wheel
If your steering wheel feels loose or requires too much movement to control the vehicle, this could indicate excessive play in the steering gearbox. Causes include worn gears, loose connections, or damage within the gearbox. To detect this issue, try gently moving the steering wheel while the car is stationary; noticeable lag in the response of the wheels suggests a problem. Ignoring this issue can lead to reduced steering precision and compromised safety.
Steering Wheel Binding or Stiffness
A binding or stiff steering wheel makes it difficult to maneuver the vehicle, especially at lower speeds. This issue often results from insufficient lubrication, internal damage to the gearbox, or worn-out bearings. Troubleshooting includes checking the power steering fluid levels and inspecting the gearbox for wear or obstructions. Addressing these causes promptly can restore the smooth functioning of your steering system.
Fluid Leaks
Leaks are a clear sign of trouble within a steering gearbox. Hydraulic steering systems rely on power steering fluid for smooth operation. Leaks typically occur due to worn seals or damaged hoses. You might notice fluid pooling under your car or experience increased steering effort. Ignoring leaks can lead to further damage, including overheating or complete failure of the gearbox.
By addressing these issues early, you can extend the lifespan of your steering gearbox and maintain optimal vehicle performance.
Maintenance and Adjustment Tips for Steering Gearboxes

Proper maintenance of your steering gearbox is essential for safe and efficient vehicle performance. Here are three key areas to focus on:
Regular Inspections
Routine checks can help identify issues before they escalate. During inspections, look for signs of wear and tear, such as cracks in the housing, loosened components, or rust. Pay attention to excessive play in the steering wheel or unusual noises while turning. Regularly inspect the seals and hoses for leaks, especially in hydraulic systems. Addressing these small issues promptly can prevent costly repairs and extend the lifespan of your gearbox.
Adjusting the Steering Gearbox
Over time, a steering gearbox may require adjustments to maintain optimal performance. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide for adjusting the worm bearing preload and sector lash:
- Park the vehicle on a flat surface and disconnect the battery for safety.
- Locate the adjustment screws on the gearbox. Typically, one adjusts the worm bearing preload, and the other manages the sector shaft lash.
- Turn the preload screw clockwise to reduce play, ensuring it’s snug but not overly tight.
- Adjust the sector shaft lash screw gradually to eliminate excessive movement. Avoid overtightening, as this could cause binding.
- Reconnect the battery and test the steering system for smoothness.
If adjustments seem complicated, consult a professional to avoid potential risks.
Lubrication Practices
Lubrication is critical to preventing wear and binding in a steering gearbox. Always use the manufacturer-recommended grease or fluid, and apply it according to the specified intervals. In hydraulic systems, check the power steering fluid regularly and replace it as necessary. Ensure that seals are intact to prevent leaks, which can compromise lubrication.
By performing regular inspections, making necessary adjustments, and maintaining proper lubrication, you can keep your steering gearbox in excellent condition for years.
Replacement and Repair Considerations for Steering Gearboxes
A time will come when repairing your steering gearbox is no longer viable, and replacement becomes necessary. Understanding when and how to replace this critical component can save you time, money, and hassle.
When to Replace the Steering Gearbox
Several signs may indicate the need for replacement. If you notice persistent excessive play in the steering wheel, grinding noises, or stiffness that adjustments and lubrication fail to fix, it might be time for a new gearbox. Leaks in hydraulic systems that recur after repairs and significant internal damage, such as cracked housings or stripped gears, also warrant replacement. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to dangerous steering failures.
Choosing the Right Replacement
When selecting a replacement, consider factors like compatibility, quality, and cost. A new steering gearbox provides the most reliability, but remanufactured options can be more cost-effective without sacrificing performance. Ensure the part matches your vehicle’s specifications, including the type of steering system (manual or power). Look for warranties and trusted brands to guarantee quality and longevity.
DIY vs. Professional Repair
Replacing a steering gearbox yourself can save money, but it’s a complex job that requires mechanical expertise and proper tools. DIY repair involves heavy components and precise alignment, making it risky for inexperienced individuals. On the other hand, hiring a professional ensures the job is done correctly and safely, albeit at a higher cost. If you’re unsure about your skills, opting for professional repair is the safest choice.
By recognizing the signs of failure, selecting the right replacement, and making informed decisions about repair methods, you can maintain a reliable and responsive steering system.
Advancements in Steering Gearbox Technology

Modern vehicles are redefining the way we steer, thanks to technological advancements in steering gearboxes. Two key innovations—Electric Power Steering (EPS) systems and their integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)—are driving these changes.
Electric Power Steering (EPS) Systems
Unlike traditional hydraulic systems, EPS systems rely on electric motors to assist steering. This eliminates the need for power steering fluid, reducing maintenance and the risk of leaks. EPS systems are lighter, more energy-efficient, and provide better fuel economy. They also allow for more precise control, making them ideal for modern vehicles that require agility and responsiveness. Additionally, EPS enables customizable steering feel, with manufacturers offering modes for sportier or more relaxed driving.
Integration with Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
The evolution of ADAS features, such as lane-keeping assistance, adaptive cruise control, and automated parking, has transformed the role of steering gearboxes. Modern systems integrate seamlessly with electronic control units (ECUs) to enable semi-autonomous driving functions. For instance, steering adjustments are made automatically to keep the car centered in its lane or to maneuver in tight spaces. These advancements not only enhance convenience but also improve safety by reducing driver errors.
By combining the efficiency of EPS systems with the intelligence of ADAS, steering gearboxes have become integral to the future of driving. These innovations make vehicles safer, more efficient, and better suited to the demands of modern transportation.
Conclusion
The steering gearbox is a vital component that ensures precise control and safe maneuverability of your vehicle. Understanding its functions, common issues, and maintenance requirements empowers you to keep your steering system in optimal condition. Regular inspections, timely adjustments, and staying informed about advancements like Electric Power Steering (EPS) and ADAS integration can enhance your driving experience and safety. Whether you’re addressing repairs or considering a replacement, prioritizing the health of your steering gearbox contributes to your vehicle’s performance and longevity, ensuring smooth and confident driving for years to come.
Steering Gearboxe Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is a steering gearbox, and why is it important?
A steering gearbox is a critical component of the steering system that converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into the linear motion needed to turn the wheels. It ensures precise control, smooth handling, and safety while driving.
2. What are the signs of a failing steering gearbox?
Common signs include excessive play in the steering wheel, stiffness or binding during turns, grinding noises, and fluid leaks. If these issues persist, it may be time for a repair or replacement.
3. How often should I check or maintain my steering gearbox?
Regular inspections are recommended every 6-12 months or during routine vehicle servicing. Ensure lubrication is adequate, seals are intact, and there are no signs of wear or leaks.
4. Can I adjust my steering gearbox myself?
Yes, minor adjustments like tightening the worm bearing preload or sector lash are possible if you have the tools and mechanical knowledge. However, improper adjustments can cause binding or damage, so consult a professional if unsure.
5. What’s the difference between hydraulic and electric power steering gearboxes?
Hydraulic systems use fluid pressure to assist steering, while electric power steering (EPS) systems use electric motors. EPS is more energy-efficient, requires less maintenance, and integrates better with modern vehicle technologies like ADAS.
6. Is it better to repair or replace a faulty steering gearbox?
This depends on the extent of the damage. Minor issues like leaks or worn seals can often be repaired. However, severe damage, such as cracked housings or stripped gears, typically requires a replacement.
7. What factors should I consider when choosing a replacement steering gearbox?
Ensure compatibility with your vehicle, prioritize quality parts, and decide between new or remanufactured gearboxes based on your budget and needs. Look for trusted brands and warranty options.