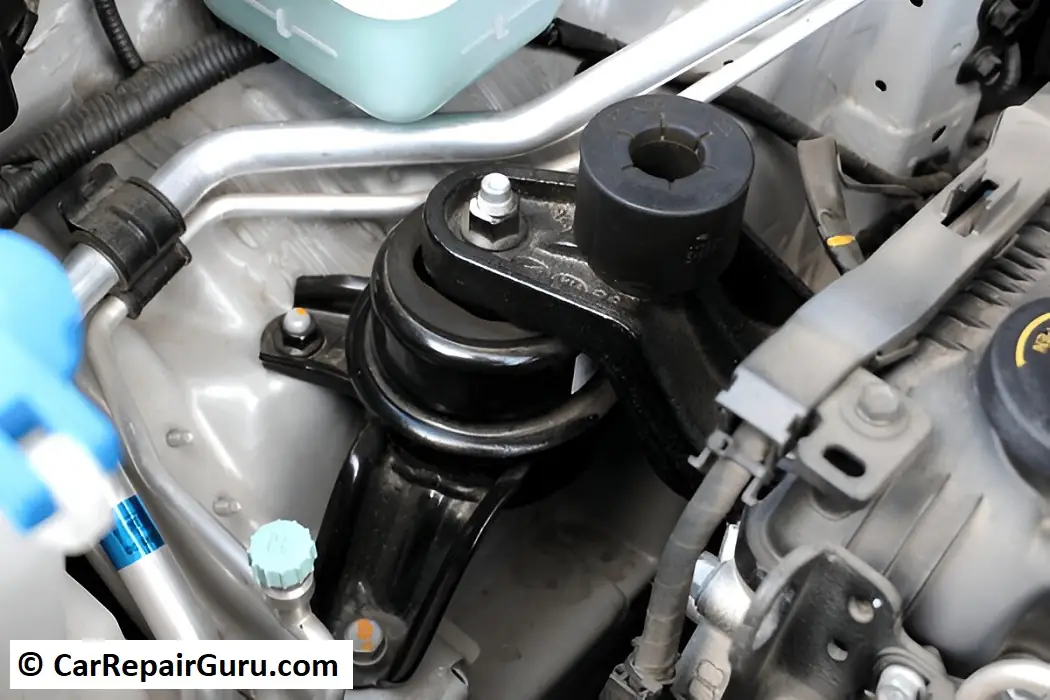
Imagine feeling strong vibrations, hearing knocking sounds, or seeing your engine shift oddly while driving. These signs often point to a failing car engine mount—a small but vital part that keeps your vehicle running smoothly.
Engine mounts secure the engine in place and absorb shocks from the road. They also maintain proper alignment between the engine and transmission, helping your car perform optimally.
Over time, engine mounts wear out due to heat, rough driving, and age. When damaged, they cause vibrations, noise, and engine movement that can harm your vehicle’s performance and lifespan. This guide covers everything about engine mounts—from their role and types to symptoms, replacement, and maintenance.
- Functions of Engine Mounts
- Types of Car Engine Mounts
- Common Symptoms of a Failing Car Engine Mount
- Causes of Engine Mount Failure
- Inspection and Diagnosis
- Step-by-Step Guide to Engine Mount Replacement
- Preparation: Getting Ready for the Replacement
- Replacement Process: Removing and Installing the New Mount
- Post-Installation Checks: Ensuring Proper Functionality
- Engine Mount Replacement Cost & Considerations
- Preventive Maintenance Tips
- Conclusion
- FAQ
Functions of Engine Mounts
The car engine mount plays a vital role in keeping your vehicle running smoothly. While it may seem like a simple component, its function goes beyond just holding the engine in place. Let’s break down its key roles:
1. Supporting the Engine’s Weight and Maintaining Alignment
Engines are heavy, and without proper support, they would shift or tilt under their own weight. Engine mounts are designed to securely attach the engine to the car’s frame, ensuring it stays in the correct position. Proper alignment between the engine and transmission is essential for smooth power delivery, efficient fuel consumption, and overall vehicle stability.
2. Absorbing and Dampening Engine Vibrations
Engines generate a lot of movement and vibration during operation. Without engine mounts, this vibration would transfer directly to the car’s cabin, making for an uncomfortable ride. Most car engine mounts are made of rubber or contain hydraulic fluid to effectively dampen engine vibration and reduce noise. In modern vehicles, electronic engine mounts further enhance vibration control by adjusting stiffness based on driving conditions.
3. Protecting Other Engine Components
Excessive engine movement can put stress on surrounding components such as hoses, belts, and exhaust systems. A worn-out engine mount can cause misalignment, leading to premature wear and costly repairs. By securing the engine in place, engine mounts prevent unnecessary strain on these parts, prolonging their lifespan and keeping your car running efficiently.
Understanding these functions highlights why regular engine mount inspection is essential to prevent costly damage and ensure a smooth driving experience.
Types of Car Engine Mounts
Not all car engine mounts are the same. Different types are designed to cater to various driving needs, vehicle designs, and performance expectations. Here’s a closer look at the most common types:
1. Solid Rubber Mounts – Cost-Effective and Durable
One of the most widely used types, solid rubber engine mounts are made of heavy-duty rubber bonded to metal brackets. They are designed to absorb engine vibration and reduce noise while being highly durable. These mounts are cost-effective and ideal for everyday vehicles. However, they may not provide as much vibration dampening as hydraulic or electronic mounts.
2. Hydraulic Engine Mounts – Enhanced Vibration Absorption
Hydraulic mounts contain a fluid-filled chamber that helps absorb engine vibrations more effectively than rubber mounts. These are commonly found in luxury and high-performance cars, where ride comfort is a priority. Over time, these mounts may develop leaks, reducing their efficiency and requiring engine mount replacement.
3. Electronic Engine Mounts – Adaptable Vibration Control
Advanced electronic engine mounts use sensors to adjust stiffness based on driving conditions. These mounts are found in modern vehicles, where precise control over engine movement is necessary to enhance ride quality and efficiency. While they offer superior comfort, they are more expensive and complex to replace.
4. Polyurethane Mounts – A Balance Between Performance and Longevity
For those who seek enhanced durability and performance, polyurethane engine mounts offer a stiffer alternative to rubber. They are commonly used in sports cars and modified vehicles, as they reduce excessive engine movement. However, they may transmit more vibrations to the cabin.
5. Transmission Mounts – Supporting the Entire Drivetrain
Though not directly an engine mount, transmission mounts play a crucial role in securing both the engine and transmission. A failing transmission mount can lead to misalignment, excessive vibrations, and poor drivetrain performance.
Choosing the right car engine mount depends on your vehicle type, driving style, and comfort preferences. Regular inspections ensure they function properly and extend their lifespan.
Common Symptoms of a Failing Car Engine Mount

A worn or damaged car engine mount can lead to serious issues that affect your vehicle’s performance and comfort. If left unchecked, a failing engine mount can cause excessive engine movement, vibrations, and even damage to surrounding components. Here are the most common warning signs to watch out for:
1. Increased Engine Vibration or Excessive Shaking
One of the earliest and most noticeable signs of a failing engine mount is excessive engine vibration. Since engine mounts are designed to absorb and dampen vibrations, a broken or worn-out mount can no longer perform this function effectively. As a result, you may feel unusual shaking in the cabin, especially when idling or accelerating.
2. Loud Clunking or Knocking Noises
If you hear clunking, banging, or knocking sounds when accelerating, braking, or making turns, it could indicate a damaged engine mount. These noises occur when the engine shifts excessively due to a failing mount, causing it to make contact with other components under the hood. This is a serious issue that should be addressed immediately to prevent further damage.
3. Visible Cracks or Wear on the Engine Mount Bracket
Regular visual inspections of your engine mounts can help identify early signs of wear. Look for cracks, torn rubber, or leaking hydraulic fluid (if you have hydraulic mounts). A worn-out engine mount bracket will be less effective at securing the engine, increasing the risk of failure.
4. Engine Shifting or Tilting Unnaturally
A failing engine mount may cause the engine to shift, lean, or tilt abnormally when accelerating or decelerating. If you notice unusual engine movement when opening the hood, it’s a strong indicator that one or more of the engine mounts need replacing.
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to severe engine damage, misalignment, and costly repairs. If you experience any of these signs, it’s best to have your engine mounts inspected and replaced if necessary.
Causes of Engine Mount Failure
Like any other car component, engine mounts are subject to wear and tear over time. Several factors contribute to their deterioration, affecting their ability to stabilize the engine and absorb vibrations. Here are the most common causes of engine mount failure:
1. Wear and Tear Due to Prolonged Use
Over time, car engine mounts degrade naturally due to constant exposure to engine vibrations, weight pressure, and movement. The rubber or polyurethane material in the mounts can harden, crack, or lose elasticity, reducing their ability to absorb shocks effectively.
2. Exposure to Extreme Temperatures
High heat from the engine, combined with external temperature fluctuations, can weaken engine mounts over time. Rubber mounts are especially vulnerable, as excessive heat causes them to dry out and crack, while extreme cold can make them brittle.
3. Fluid Leaks Affecting Hydraulic Mounts
Hydraulic engine mounts contain a fluid-filled chamber that helps absorb vibrations. However, leaks from the mount or surrounding components can reduce the fluid level, making the mount less effective. A leaking hydraulic mount often leads to increased engine vibration and instability.
4. Aggressive Driving Habits
Frequent hard acceleration, sudden braking, and driving over rough terrain can put extra stress on engine mounts, causing them to deteriorate faster. Aggressive driving leads to excessive engine movement, which accelerates wear and increases the risk of mount failure.
By understanding these causes, drivers can take preventive measures such as regular inspections and smoother driving habits to extend the lifespan of their engine mounts and maintain vehicle performance.
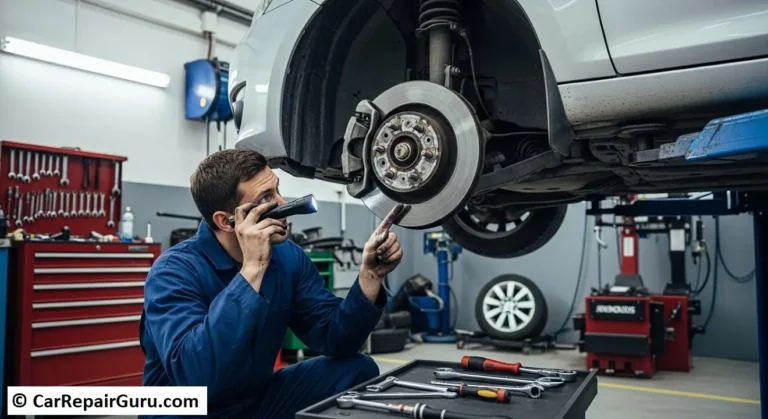
Inspection and Diagnosis
Regular inspection of your car engine mounts can help detect potential issues before they lead to major problems. Here’s how to assess the condition of your engine mounts and diagnose failures effectively.
1. Visual Inspection for Cracks or Damage
A quick visual inspection can reveal signs of wear and tear. Here’s what to check:
- Look for cracks, tears, or separation in the rubber material of the engine mount.
- If you have hydraulic engine mounts, check for fluid leaks, which indicate a failing mount.
- Inspect the metal brackets and bolts for rust, looseness, or visible misalignment.
If any of these signs are present, it’s time to consider an engine mount replacement.
2. Identifying Excessive Engine Movement
A simple test can help detect engine mount failure:
- Start your engine and watch for excessive movement under the hood. The engine should remain stable.
- Put the car in drive or reverse while pressing the brake and gently rev the engine. If the engine shifts excessively, the mounts may be worn out.
- Listen for clunking or knocking sounds when accelerating or braking, as they could indicate that the engine is shifting due to a failing mount.
3. Professional Diagnostic Methods
For a precise diagnosis, mechanics use engine vibration testing tools to measure the intensity of vibrations. They may also use chassis lifts to examine the mounts from underneath and check for alignment issues.
If you suspect a failing engine mount, early detection can prevent further damage to your engine and transmission. Replacing worn-out mounts on time ensures a smoother ride, reduces engine vibration, and prevents costly repairs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Engine Mount Replacement

If you notice excessive engine vibration, clunking noises, or visible cracks in your car engine mount, it may be time for a replacement. Here’s a step-by-step guide to replacing an engine mount safely and effectively.
Preparation: Getting Ready for the Replacement
1. Necessary Tools and Safety Precautions
Before starting, gather the following tools:
✔️ Jack and jack stands – To lift and support the engine.
✔️ Socket wrench set – For loosening and tightening mount bolts.
✔️ Torque wrench – To ensure proper bolt tightness.
✔️ Wooden block – To prevent damage when lifting the engine.
✔️ Protective gloves and safety glasses – To ensure safety.
⚠️ Safety Tip: Always work on a level surface, engage the parking brake, and disconnect the battery before starting.
2. Locating the Faulty Engine Mount
- Open the hood and inspect all engine mounts (usually 2-4 in most cars).
- Identify the one with visible cracks, leaks (for hydraulic mounts), or loose bolts.
- Refer to your vehicle’s manual for exact engine mount locations.
Replacement Process: Removing and Installing the New Mount
1. Lifting the Engine Securely
- Use a car jack to lift the vehicle if needed for better access.
- Place a wooden block under the oil pan, then gently lift the engine with a jack to relieve pressure on the mount.
2. Removing the Old Engine Mount
- Use a socket wrench to loosen and remove the bolts securing the mount to the engine and chassis.
- Carefully slide the old mount out, ensuring no damage to nearby components.
3. Installing the New Engine Mount
- Position the new engine mount in place, ensuring correct alignment.
- Hand-tighten the bolts first, then use a torque wrench to secure them to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Post-Installation Checks: Ensuring Proper Functionality
1. Checking Alignment and Securing Bolts
- Double-check that the mount sits evenly, with no misalignment.
- Ensure all bolts are tightened to prevent future issues.
2. Testing the Vehicle for Reduced Vibration
- Start the engine and observe for excessive movement or noise.
- Take a short test drive to ensure a smoother ride and minimal vibrations.
3. When to Consult a Professional Mechanic
If you’re unsure about lifting the engine safely or notice persistent vibration or alignment issues, it’s best to seek help from a certified mechanic. Properly installed engine mounts ensure a more stable, quieter, and longer-lasting ride.
Engine Mount Replacement Cost & Considerations
Replacing a car engine mount is an essential repair that affects engine stability and overall driving comfort. The cost of engine mount replacement varies depending on several factors, including vehicle type, labor charges, and mount material.
1. Average Cost Range for Engine Mount Replacement
- On average, replacing an engine mount costs between $200 to $700 per mount.
- Parts alone typically range from $50 to $250, depending on the type (solid rubber, hydraulic, or electronic mounts).
- Labor costs can add another $150 to $500, depending on the complexity of the job.
2. Factors Affecting the Total Engine Mount Repair Cost
Several factors can influence the final replacement cost, including:
✔️ Vehicle Make & Model: Luxury or high-performance vehicles often have more complex mounting systems, increasing labor costs.
✔️ Number of Mounts Replaced: Most vehicles have two to four engine mounts; replacing multiple mounts increases costs.
✔️ Type of Engine Mount: Hydraulic and electronic mounts are more expensive than traditional rubber mounts.
✔️ Labor Charges: Independent mechanics may charge less than dealership services.
3. DIY vs. Professional Engine Mount Installation
✅ DIY Replacement: If you have mechanical experience, you can save on labor costs by replacing the engine mount yourself. However, improper installation can cause severe engine misalignment and additional repairs.
✅ Professional Installation: A mechanic ensures precise mount alignment, proper torque specifications, and overall safety. If you’re unsure about lifting the engine or tightening mounts correctly, professional installation is the safer option.
Considering both cost and expertise, DIY may be cost-effective, but professional installation guarantees long-term reliability and vehicle safety.
Preventive Maintenance Tips
Proper maintenance of car engine mounts can extend their lifespan and prevent costly repairs. Follow these preventive measures to keep your engine mounts in top condition.
1. Routine Inspection Schedules
- Inspect engine mounts every 20,000 to 30,000 miles or during regular oil changes.
- Look for cracks, leaks (for hydraulic mounts), or excessive wear.
- If you notice unusual engine movement or increased vibration, get a professional inspection.
2. Avoid Aggressive Driving to Prevent Engine Mount Damage
- Sudden hard acceleration or braking puts excessive stress on the engine mounts, causing them to wear out faster.
- Avoid driving over potholes or rough terrain at high speeds, as impact forces can weaken the mounts.
- If your vehicle is performance-tuned, consider reinforced engine mounts to handle higher stress levels.
3. Address Minor Engine Mount Noises Before They Worsen
- If you hear clunking or knocking noises, inspect the mounts immediately.
- Replacing a worn-out engine mount early prevents strain on the engine and transmission system.
- Addressing minor vibration issues early can help avoid damage to surrounding engine components.
Regular maintenance ensures smoother rides, reduced engine vibrations, and longer-lasting engine mounts.
Conclusion
Car engine mounts play a crucial role in stabilizing the engine, reducing vibrations, and ensuring a smooth driving experience. A failing engine mount can lead to excessive engine movement, increased cabin vibration, and potential damage to surrounding components. Addressing engine mount issues early prevents costly repairs and enhances overall vehicle performance.
Regular inspection and maintenance are key to prolonging the lifespan of engine mounts. Checking for visible cracks, leaks, or unusual engine movement can help detect issues before they worsen. Avoiding aggressive driving habits and replacing worn-out mounts on time ensures a safer, quieter, and more comfortable ride.
If you experience engine shaking, clunking noises, or shifting, it’s essential to diagnose the problem and take action. Whether you choose DIY replacement or professional installation, keeping your engine mounts in good condition will help maintain the overall health of your vehicle for years to come.
FAQ
Q1: How long do car engine mounts last?
A: On average, car engine mounts last between 5 to 7 years, depending on driving conditions and vehicle maintenance.
Q2: Can I drive with a broken engine mount?
A: It is not advisable, as a damaged engine mount can cause excessive vibrations, potential engine misalignment, and further damage to the vehicle’s components.
Q3: What are the signs of a bad engine mount?
A: Symptoms include excessive engine vibration, knocking sounds, and noticeable engine movement under the hood.
Q4: How much does it cost to replace an engine mount?
A: The cost ranges from $200 to $600, depending on the vehicle model and labor charges.
Q5: Are polyurethane engine mounts better than rubber mounts?
A: Polyurethane mounts offer better durability and performance but may transmit more vibrations compared to rubber engine mounts.






