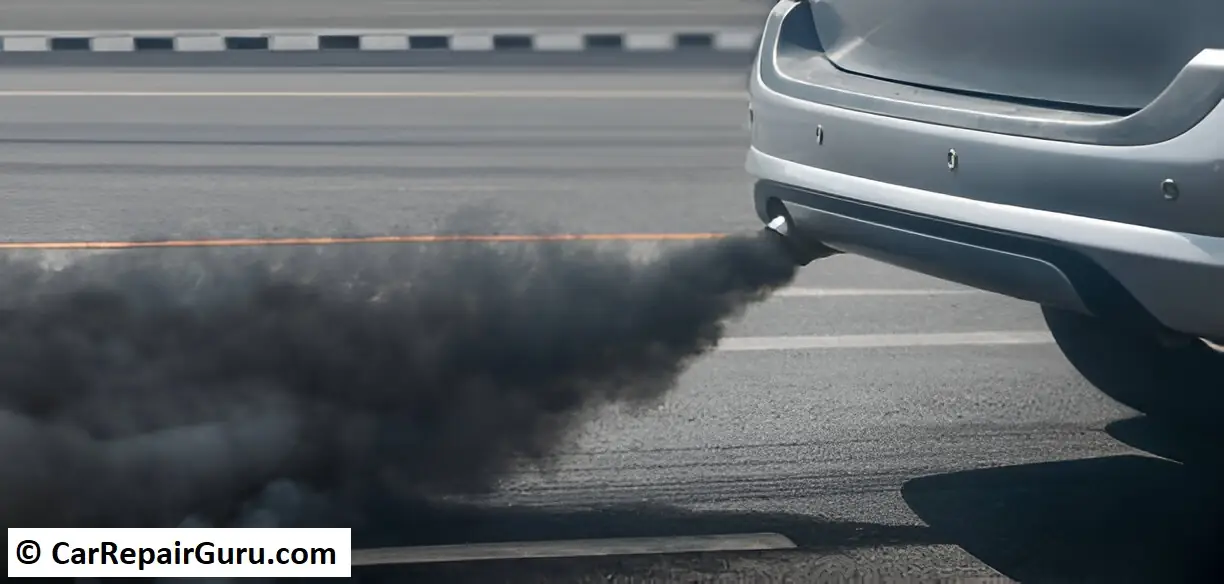
Black smoke from engines is a common yet concerning issue that can indicate serious problems with your vehicle. If your engine is emitting black smoke, it’s more than just a visual nuisance—it’s a sign of inefficiency, potential damage, and harmful emissions. Understanding the causes and effects of black smoke is crucial for diagnosing the problem early and preventing costly repairs.
In this guide, we’ll break down the causes, impacts, and solutions for black smoke emission, helping you diagnose and address the issue effectively. Whether you’re a car enthusiast, a professional mechanic, or simply a concerned driver, understanding black smoke is crucial for maintaining a healthy engine and avoiding costly repairs.
What Does Black Smoke from an Engine Indicate?
Black smoke coming from an engine is a clear sign that something isn’t working as it should. In most cases, it points to incomplete combustion—a situation where fuel isn’t fully burned in the engine. This produces excessive carbon particles, which are expelled as black smoke through the exhaust system.
For diesel engines, black smoke is relatively common but still concerning. Diesel engines rely on precise air and fuel mixing. When there’s too much fuel or insufficient air, incomplete combustion occurs. Causes might include clogged air filters, faulty fuel injectors, or worn-out turbochargers.
In gasoline engines, black smoke is less common but equally problematic. It often suggests an issue with the air-fuel ratio. Malfunctioning fuel injectors, a dirty carburetor (in older engines), or a damaged oxygen sensor could be the culprit.
Beyond mechanical issues, using low-quality fuel or failing to maintain the engine regularly can also contribute to black smoke.
While occasional smoke might not seem alarming, consistent black smoke should never be ignored. It not only harms the environment by increasing emissions but also reduces your vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency, signaling the need for immediate inspection and repair.
Common Causes of Black Smoke Emission

Black smoke from an engine is often a symptom of underlying mechanical or maintenance issues. Understanding the common causes can help pinpoint and resolve the problem effectively.
Clogged Air Filters
Air filters play a critical role in maintaining the correct air-fuel mixture for combustion. When the air filter becomes clogged with dirt and debris, it restricts airflow to the engine. This lack of air causes an imbalance in the air-fuel mixture, leading to incomplete combustion. The result? Excess unburned fuel is expelled as black smoke. Regularly replacing or cleaning the air filter is essential to prevent this issue and ensure optimal engine performance.
Faulty Fuel Injectors
Fuel injectors are responsible for delivering the precise amount of fuel needed for combustion. If an injector becomes damaged, clogged, or stuck open, it can spray too much fuel into the combustion chamber. This over-fueling results in incomplete combustion, producing thick black smoke. Faulty injectors not only increase emissions but also reduce fuel efficiency and engine power.
Engine Deposits
Over time, carbon deposits can build up in the engine’s combustion chamber, intake valves, and fuel injectors. These deposits interfere with the combustion process, reducing the efficiency of fuel burning. The engine may struggle to maintain the correct air-fuel ratio, resulting in black smoke emission. Using quality fuel and periodic engine cleaning can minimize carbon buildup.
Damaged Carburetors (in Older Engines)
Carburetors, found in older vehicles, control the mixing of air and fuel for combustion. If the carburetor is damaged or improperly adjusted, it can cause an overly rich fuel mixture, leading to black smoke. Worn-out components or leaks within the carburetor further exacerbate the problem. While modern vehicles rely on fuel injection systems, maintaining or repairing carburetors in older models is critical for smoke-free operation.
Exhaust System Restrictions
Blockages in the exhaust system, such as a clogged catalytic converter or muffler, can create backpressure. This backpressure disrupts the combustion process and forces unburned fuel to exit through the exhaust as black smoke. Additionally, restricted exhaust flow may cause the engine to work harder, leading to reduced performance and higher fuel consumption. Regular inspections and timely repairs of the exhaust system are necessary to avoid such issues.
By addressing these common causes, you can restore your engine’s efficiency, reduce emissions, and prevent further damage to vital components.
Effects of Black Smoke on Engine Performance
Black smoke from an engine isn’t just a visual nuisance—it has significant implications for your vehicle’s performance, efficiency, and the environment.
Reduced Fuel Efficiency
One of the most immediate effects of black smoke is reduced fuel efficiency. Black smoke often indicates incomplete combustion, meaning that not all the fuel is being converted into energy. This unburned fuel is wasted, forcing the engine to consume more fuel to produce the same power output. Over time, this leads to higher fuel costs and more frequent refueling.
Engine Health Deterioration
Persistent black smoke can take a toll on your engine’s health. The buildup of carbon deposits in the combustion chamber, intake valves, and exhaust system can reduce engine efficiency and performance. These deposits can also lead to increased wear and tear on critical components, such as pistons, cylinders, and turbochargers. If left unresolved, the engine may experience reduced power, rough idling, and eventual failure of key parts, requiring costly repairs or replacements.
Environmental Impact
From an environmental perspective, black smoke is a major contributor to air pollution. It contains high levels of particulate matter and other harmful emissions that degrade air quality. These pollutants can contribute to respiratory problems and other health issues in humans and animals. Additionally, excessive black smoke emissions from diesel vehicles are a violation of emissions standards in many regions, potentially leading to fines or failed inspections.
Decreased Overall Performance
The presence of black smoke often signals underlying issues that hinder overall engine performance. Whether it’s sluggish acceleration, reduced towing capacity, or difficulty maintaining speed, these performance problems can make driving less enjoyable and more stressful.
By addressing the causes of black smoke promptly, you can restore your engine’s health, improve fuel efficiency, and minimize your vehicle’s environmental footprint. Regular maintenance and timely repairs are key to keeping your engine running smoothly and smoke-free.
Diagnosing the Cause of Black Smoke

Diagnosing the cause of black smoke from an engine is essential to restore optimal performance and prevent further damage. Here’s a step-by-step approach to identifying the root of the problem.
Visual Inspection
Begin with a basic visual inspection of your vehicle:
- Check the Color of the Smoke: Black smoke indicates incomplete combustion, often due to excess fuel or insufficient air.
- Inspect Under the Hood: Look for obvious issues like loose or damaged hoses, leaking fuel lines, or soot around the exhaust pipe.
- Look for Warning Lights: Modern vehicles have onboard diagnostic systems. If the “Check Engine” light is on, use a diagnostic tool to retrieve error codes that can guide you to the problem.
A thorough visual inspection helps rule out surface-level issues before diving deeper.
Checking Air Filters and Fuel Injectors
Air filters and fuel injectors are two common culprits of black smoke:
- Air Filter: Remove the air filter and check if it’s clogged with dirt or debris. A dirty filter restricts airflow, leading to incomplete combustion. Clean or replace the filter as needed.
- Fuel Injectors: Test the fuel injectors for proper function. Clogged or damaged injectors can spray too much fuel into the combustion chamber. This can often be resolved by using a fuel injector cleaner or having the injectors professionally serviced.
Addressing these components often resolves black smoke issues related to the air-fuel mixture.
Evaluating Exhaust System
The exhaust system plays a key role in removing waste gases efficiently:
- Inspect for Blockages: A clogged catalytic converter, muffler, or exhaust pipe can create backpressure, disrupting combustion and causing black smoke.
- Listen for Signs: Odd sounds, like hissing or rattling, can indicate exhaust system damage.
- Professional Diagnostics: If you suspect a blockage, consult a mechanic to inspect and clear the system safely.
By following these steps, you can identify and resolve the underlying issues causing black smoke. Regular maintenance of these components can help prevent the recurrence of smoke and ensure a healthier engine.
Solutions to Reduce Black Smoke Emission
Reducing black smoke emissions from your engine is crucial for improving performance, fuel efficiency, and environmental sustainability. Implementing the following solutions can help resolve the issue and prevent it from recurring.
Regular Maintenance Practices
Routine maintenance is the foundation of a healthy, smoke-free engine.
- Inspect and Replace Air Filters: Ensure air filters are clean and free from debris. Clogged filters disrupt the air-fuel mixture, leading to black smoke. Replace them as recommended by your vehicle’s manual.
- Monitor Fuel Injectors: Regularly check and clean fuel injectors to prevent over-fueling or incomplete combustion. Use a fuel injector cleaner to dissolve deposits that can clog injectors.
- Oil and Filter Changes: Dirty oil can contribute to carbon buildup in the engine. Stick to a consistent oil change schedule to keep internal components clean and lubricated.
- Check Turbochargers: For diesel engines, ensure the turbocharger is functioning properly to maintain optimal air pressure. A failing turbo can lead to incomplete combustion and black smoke.
Using Quality Fuel and Additives
The quality of fuel directly impacts combustion efficiency and emissions.
- Opt for High-Quality Fuel: Premium fuels often contain fewer impurities and burn more cleanly, reducing the chances of black smoke.
- Fuel Additives: Specialized additives can clean fuel injectors, prevent carbon buildup, and improve combustion. Look for additives designed for your engine type and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for usage.
- Avoid Contaminated Fuel: Always refuel from reputable stations to minimize the risk of contaminants entering your engine.
Professional Engine Tuning
Professional tuning can significantly enhance your engine’s efficiency and reduce black smoke.
- Optimize the Air-Fuel Mixture: A mechanic can adjust the air-fuel ratio to ensure complete combustion. Modern vehicles with electronic control units (ECUs) can be reprogrammed to optimize engine performance.
- Inspect and Replace Worn Components: A professional can identify and replace damaged parts, such as faulty fuel injectors, turbochargers, or exhaust components, that may be contributing to black smoke.
- Test and Align Sensors: Faulty oxygen or mass airflow sensors can misread data and cause improper fuel injection. Professional calibration of these sensors can resolve such issues.
By prioritizing regular maintenance, using quality fuel, and investing in professional tuning, you can effectively reduce black smoke emissions. These practices not only extend the life of your engine but also ensure better fuel economy and a cleaner environment.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Black Smoke

Preventing black smoke from your engine is not only better for your vehicle’s performance but also for your wallet and the environment. Following these key preventive measures can help you maintain a smoke-free engine.
Adhering to Ma
nufacturer’s Guidelines
Every vehicle comes with a set of manufacturer-recommended maintenance schedules and practices tailored to its specific design.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Regular servicing as outlined in your owner’s manual ensures components like air filters, fuel injectors, and exhaust systems are checked and replaced on time.
- Use Specified Parts: Always use recommended parts and fluids to maintain the engine’s optimal performance. For example, the wrong type of oil or filters can disrupt combustion efficiency and lead to black smoke.
- Timely Repairs: Address minor issues immediately to prevent them from escalating into serious problems, such as clogged injectors or worn-out turbochargers.
Monitoring Engine Performance
Keeping a close eye on your engine’s performance can help identify problems early.
- Watch for Warning Signs: Pay attention to dashboard warning lights and unusual sounds or vibrations. These can indicate issues like sensor malfunctions or air-fuel imbalances.
- Check Exhaust Emissions: Occasionally observe the color of the smoke from your exhaust. Black smoke is often a precursor to larger engine troubles.
- Use Diagnostic Tools: Modern vehicles allow for engine diagnostics via OBD scanners, which can detect issues before they manifest visibly.
Ensuring Proper En gine Load
Operating your engine under the right conditions is crucial for preventing black smoke.
- Avoid Prolonged Idling: Extended idling leads to incomplete combustion and carbon buildup, increasing the risk of black smoke. Turn off the engine when stationary for long periods.
- Maintain Balanced Load: Ensure your engine isn’t overburdened by excessive weight or towing capacity. Overloading can strain the engine and disrupt combustion efficiency.
By adhering to these preventive measures, you can avoid the costly repairs and environmental damage associated with black smoke, keeping your engine in peak condition for years to come.
Conclusion
Addressing black smoke emissions is vital for maintaining engine health, improving fuel efficiency, and reducing environmental impact. Black smoke often signals incomplete combustion caused by issues like clogged air filters, faulty fuel injectors, or exhaust system blockages. Ignoring these signs can lead to decreased engine performance, higher fuel consumption, and costly repairs.
Preventive measures such as adhering to manufacturer’s guidelines, monitoring engine performance, and ensuring proper engine load can help avoid black smoke altogether. Regular maintenance, using high-quality fuel, and seeking professional tuning are effective solutions to resolve existing issues.
By prioritizing these practices, drivers can extend their engine’s lifespan, enjoy a smoother driving experience, and contribute to cleaner air. Remember, tackling black smoke promptly not only preserves your vehicle’s performance but also ensures it remains compliant with emissions standards, benefiting both you and the environment. Keep your engine in check to drive smoke-free and worry-free!
FAQs About Black Smoke from Engines
1. What causes black smoke from a diesel engine?
Black smoke from a diesel engine is often caused by incomplete combustion, typically due to clogged air filters, faulty fuel injectors, excessive carbon buildup, or turbocharger issues. It can also result from using low-quality fuel or improper engine tuning.
2. Is black smoke harmful to the engine?
Yes, black smoke indicates an underlying issue that can harm the engine over time. It can lead to carbon deposits, reduced fuel efficiency, lower performance, and increased wear on components like pistons, cylinders, and the exhaust system.
3. How can I stop my engine from emitting black smoke?
To stop black smoke, ensure regular maintenance, replace clogged air filters, clean fuel injectors, use high-quality fuel, and address any exhaust system blockages. Professional tuning or servicing may also be needed to fix underlying issues.
4. Can bad fuel quality cause black smoke?
Yes, poor-quality fuel can lead to incomplete combustion, causing black smoke. Low-grade or contaminated fuel may contain impurities that disrupt the air-fuel mixture and result in excessive emissions.
5. Should I drive my car if it emits black smoke?
While it may be safe for short distances, you should avoid prolonged driving if your car emits black smoke. The issue may worsen over time, leading to further damage, increased repair costs, and potential environmental violations. Address the problem as soon as possible.